Protein 101: Everything You Need to Know About Protein
I’ve published over 10 books on high-protein, high-fiber recipes, which are now available in more than 10 countries on Amazon. I believe protein awareness is both necessary and timeless, but the real challenge lies in finding recipes to incorporate more protein into our diets. In all my years of researching, experimenting, writing, and eating with intention, one truth keeps showing up: Protein is the most essential macronutrient most people still don’t get enough of.
This isn’t just a wellness fad. Protein awareness is rising for a reason — and the shift is changing lives. In this article, we’ll walk through what protein really is, why your body depends on it, and how to make confident choices in how you fuel your day — from breakfast smoothies to dinner bowls.
Whether you’re here to understand the science, build muscle, lose weight, improve your metabolism, or simply feel better in your body — this is your complete, no-nonsense guide to protein.
What Is Protein, Really?
Protein is one of the three macronutrients your body needs in large amounts (the others are fat and carbohydrates). But unlike carbs and fat, protein is not primarily a fuel source — it’s a builder.
At its core, protein is made of amino acids, often known as the “building blocks of life.” Your body uses these amino acids to:
- Build and repair muscles and tissues
- Create enzymes and hormones
- Support immune function
- Maintain healthy hair, skin, and nails
- Carry oxygen through your blood
- Regulate metabolism
There are 20 amino acids in total, but 9 are essential — meaning your body can’t produce them on its own, and you must get them from food.
Why Protein Awareness Is on the Rise
The movement toward high-protein eating isn’t about following a trend. It’s a response to how we feel when our diets are built around real nourishment.
Here’s why more people are turning to protein-rich meals:
- Satiety: High-protein meals keep you fuller for longer, which reduces unnecessary snacking and blood sugar spikes.
- Muscle Maintenance: As we age, protein plays a crucial role in preserving lean muscle mass, thereby protecting metabolism and mobility.
- Weight Management: Protein supports fat loss (not just weight loss) by preserving muscle while reducing body fat.
- Glucose Control: Balanced meals with protein can help manage insulin response and reduce sugar cravings.
I’ve personally experienced all of the above — more energy, fewer cravings, more vigorous workouts, and better digestion — just by consistently prioritizing protein.
How Much Protein Do You Actually Need?
This depends on your age, activity level, and goals. But the standard RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) of 0.8 grams per pound of ideal body weight (not what you weigh now) is widely considered the minimum to prevent deficiency — not the ideal target for optimal health.
For most people looking to build strength, improve body composition, or age well, a better target is:
- 0.8 to 1.2 grams of protein per pound of ideal body weight
- Or roughly 1 gram per pound — the average that works for most people and is easy to calculate
For example, if you weigh 140 lbs, you likely need between 90–150 grams of protein per day — especially if you’re active.
Complete vs. Incomplete Proteins
Not all proteins are created equal. What makes a protein “complete” is its amino acid profile.
- Complete Proteins: Contain all 9 essential amino acids in sufficient amounts.
-
Examples: Eggs, meat, fish, poultry, dairy, soy, quinoa
-
- Incomplete Proteins: Missing one or more essential amino acids.
-
Examples: Legumes, grains, nuts, seeds, vegetables
-
You don’t need every amino acid at every meal. If you eat a variety of foods throughout the day (e.g., beans + rice), your body can build the complete amino acid picture.
The Benefits of Eating More Protein
Let’s break it down.
1. Supports Muscle Growth and Repair
Protein helps rebuild muscle fibers after exercise, making you stronger over time.
2. Boosts Metabolism
Protein has a high thermic effect of food (TEF) — meaning your body burns more calories digesting it than it does carbs or fat.
3. Reduces Cravings
Meals rich in protein increase satiety hormones like peptide YY, helping you stay full and resist snacking on sugar-laden or ultra-processed foods.
4. Improves Body Composition
Protein enables you to lose fat while preserving or building lean mass, which gives you a toned, defined look.
5. Supports Aging Gracefully
As we age, we lose muscle. Prioritizing protein, especially with resistance training, helps preserve strength, independence, and bone health.
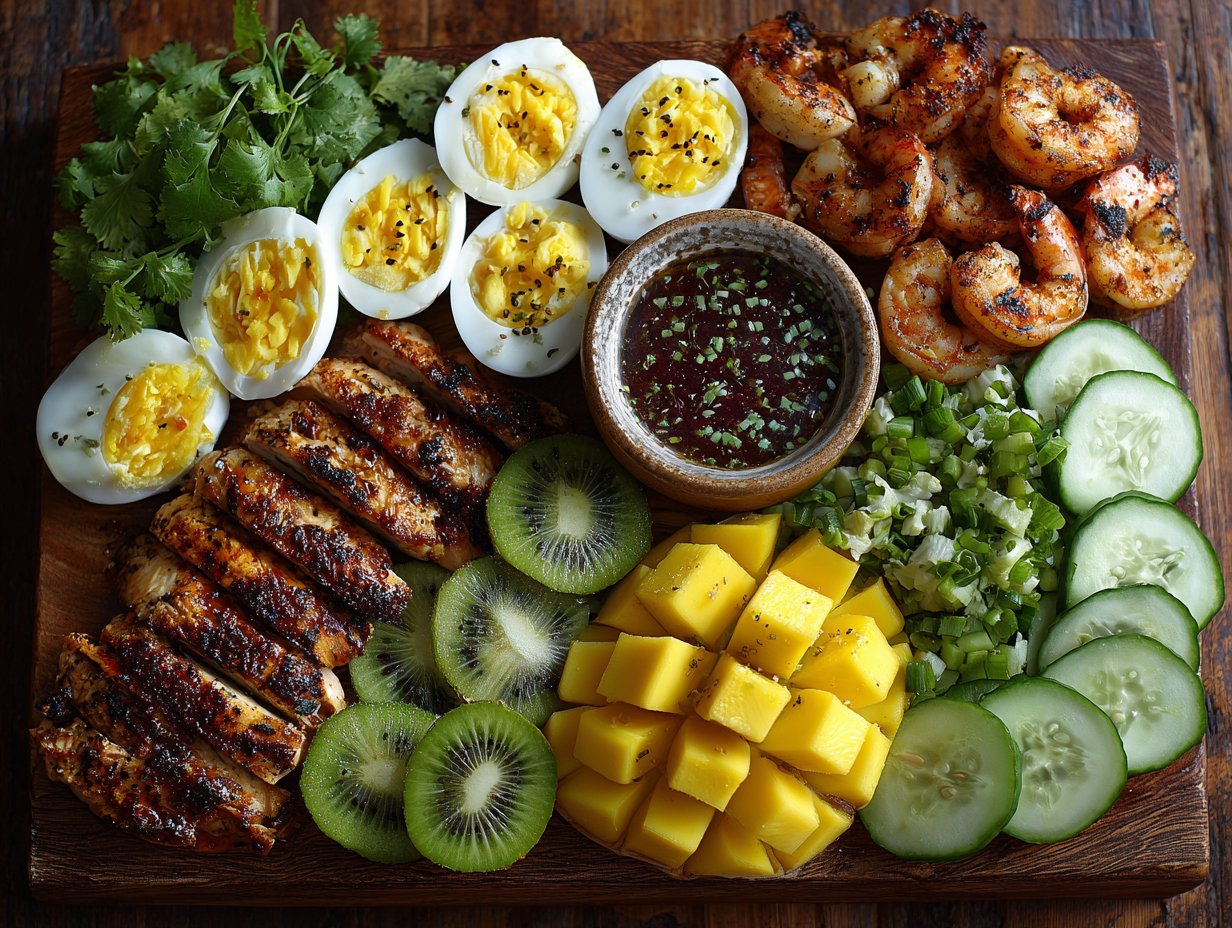
Best Protein Sources
Animal-Based (Complete Proteins)
- Eggs (especially egg whites for lean protein)
- Chicken breast, turkey
- Lean beef, bison
- Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, sardines
- Greek yogurt (fat-free or 2% for versatility)
- Cottage cheese
- Whey protein isolate or concentrate
Plant-Based
- Lentils, black beans, chickpeas
- Tofu, tempeh, edamame (soy is a complete protein)
- Quinoa
- Hemp seeds, chia seeds
- Nuts and nut butters (in moderation)
- Plant-based protein powders
In my books, I often pair legumes with whole grains to create balanced, plant-based meals that taste amazing and support muscle goals.
A Note on Protein Powders
Protein powders are not a shortcut — they’re a convenient supplement. For many busy people (including me), they’re the easiest way to hit your daily protein target.
Types of Protein Powders
- Whey Isolate: High protein, low carb, fast-absorbing
- Whey Concentrate: More affordable, slightly more carbs and fats
- Casein: Slower digesting, ideal before bed
- Plant-Based: Great for vegans; look for blends that include pea, rice, and hemp
- Collagen: Good for skin and joints, but not a complete protein
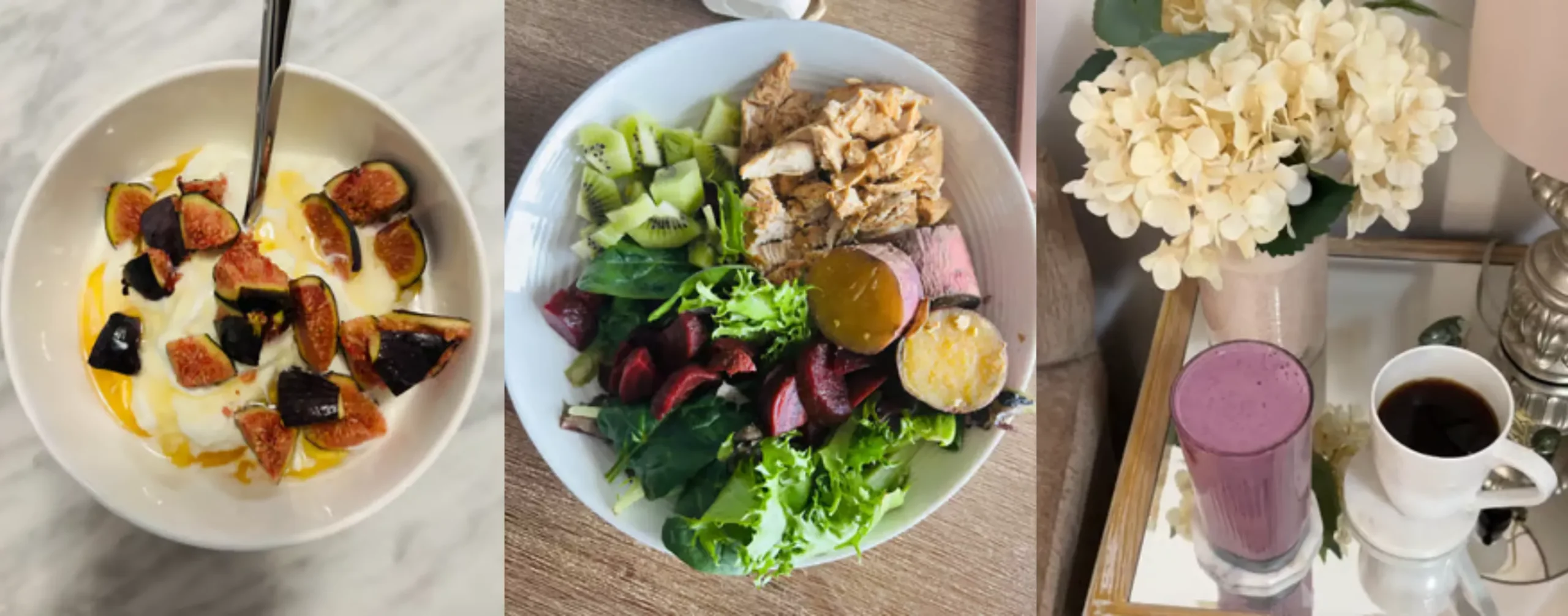
My go-to? A clean, unsweetened whey isolate in my morning smoothie (blueberries, mango, water, protein, collagen — that’s my daily start).
Protein Timing: Does It Matter?
Yes — but not obsessively. The two most important times to focus on protein are:
- First meal of the day (to set your blood sugar and hunger levels)
- Post-workout (to support muscle repair and growth)
Spreading protein evenly throughout the day is ideal — think 20–40g of protein per meal, depending on your needs.
Quick Ways to Add More Protein to Your Day
- Add a scoop of protein powder to your smoothie
- Swap sugary cereal for Greek yogurt with fruit and seeds
- Choose lean proteins for lunch and dinner (chicken, fish, tofu)
- Keep hard-boiled eggs or tuna packs in the fridge
- Mix cottage cheese into your snacks or baking
- Use protein-enriched pasta or bread for higher meals
I no longer snack, but when I did, protein-based snacks like Greek yogurt and edamame were game-changers for satiety.
Takeaway: Why I Focus on Protein Every Day
Protein isn’t just about muscles or macros. It’s about fueling a body that feels strong, stable, and vibrant.
As a writer, mother, entrepreneur, and health coach, I don’t chase perfection — I prioritize what makes a long-term difference. Protein is one of those things.
It helps me think clearly, stay energized, recover from workouts, and enjoy deeply satisfying meals without the complications.
If there’s one nutritional principle I return to over and over — for myself, my readers, and my son — it’s this:
Protein first.
Everything else falls into place more easily.
My other equal focus is on high-fiber.
More Resources from Elegant & Driven
- Not Just High in Protein: The Real Reason I Eat Greek Yogurt
- Fiber 101: Why I Always Recommend a High-Fiber Lifestyle
- The Secret to Eating Carbs Without Gaining Weight
My Favorite High-Protein Resources
My Books on Amazon
I wrote these books because I saw how powerful high-protein, high-fiber eating can be — not just for body goals, but for energy, cravings, and everyday well-being.


High-Protein High-Fiber: The Ultimate Meal Prep Solution — Packed with satisfying recipes that support gut health, metabolism, and satiety.
100g+ Protein a Day: A Real-Life Meal Prep Guide — Simple, everyday meals to help you reach 100g of protein effortlessly.
My Go-To Protein Supplements

- Whey Isolate Protein Powder – Clean, fast-absorbing, great for morning smoothies or post-workout
- Collagen Peptides – Supports joint health, skin elasticity, and adds bonus protein to your day